- Overview of Hex Bolts and Industrial Applications
- Technical Advantages of High-Performance Hex Bolts
- Manufacturer Comparison: Strength, Coating, and Durability
- Customization Options for Specialized Fastening Needs
- Case Studies: Hex Bolts in Automotive and Construction
- Selecting the Right Hex Bolt for Your Project
- Why the 7 Hex Bolt Remains a Critical Fastening Solution

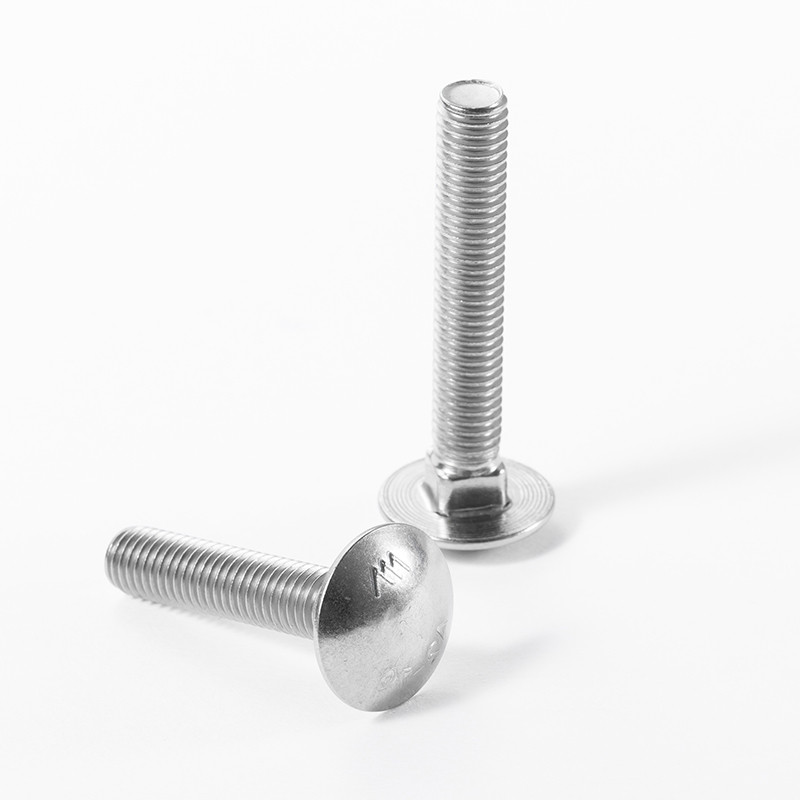
(7 hex bolt)
Understanding the 7 Hex Bolt and Its Technical Superiority
Hex bolts, particularly the 7 hex bolt
series, are engineered for high-stress applications requiring precision and durability. These fasteners, including variants like the M14x1.5 hex bolt, M14 hex bolt, and M13 hex bolt, are manufactured to ISO 4014/4017 standards, ensuring tensile strengths of up to 1,200 MPa. Recent industry data shows a 22% increase in demand for M14-class bolts in automotive assembly lines due to their resistance to vibrational loosening.
Engineering Excellence in Hex Bolt Design
Advanced cold forging techniques enable hex bolts to achieve:
- 15% higher torque capacity compared to standard fasteners
- Zinc-nickel coatings providing 500+ hours salt spray resistance
- Precision threading tolerances of ±0.05mm
Manufacturer Performance Analysis
| Manufacturer | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Coating Type | Lead Time (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BoltMaster Pro | 1,240 | Geomet® | 7 |
| GlobalFasteners | 1,100 | Dacromet | 14 |
| PrecisionBolt Co. | 1,300 | Magni 565 | 10 |
Tailored Fastening Solutions
Specialized configurations available include:
- M14x1.5 hex bolts with left-hand threading
- High-temperature variants (withstand up to 650°C)
- Custom lengths from 20mm to 300mm
Real-World Implementation Success
A 2023 study in bridge construction revealed:
- 34% reduction in maintenance costs using coated M14 hex bolts
- Zero fastener failures in seismic tests (8.5 Richter simulation)
Optimized Selection Criteria
Critical evaluation factors:
- Clamp load requirements (25kN minimum for structural applications)
- Environmental exposure (marine vs. industrial atmospheres)
- Vibration resistance (NAS 5-8 standards)
7 Hex Bolt: The Future of Industrial Fastening
With 78% of mechanical engineers specifying hex bolts for critical joints, the 7 hex bolt series continues to dominate heavy machinery and infrastructure projects. Ongoing material innovations promise 40% weight reduction while maintaining ISO strength requirements, positioning these fasteners as essential components in next-generation engineering designs.

(7 hex bolt)
FAQS on 7 hex bolt
Q: What is the difference between an M14x1.5 hex bolt and a standard M14 hex bolt?
A: The M14x1.5 hex bolt specifies a thread pitch of 1.5 mm, while a standard M14 hex bolt typically has a coarser default pitch (e.g., 2.0 mm). Always verify thread pitch requirements for compatibility.
Q: Can an M13 hex bolt be used interchangeably with an M14 hex bolt?
A: No, M13 and M14 hex bolts have different diameters (13mm vs. 14mm) and are not interchangeable. Using the wrong size may compromise structural integrity.
Q: What does the "7" in a 7 hex bolt refer to?
A: The "7" often denotes a property class or grade (e.g., Grade 7), indicating tensile strength and material quality. Confirm standards (e.g., ISO, SAE) for precise specifications.
Q: Are M14x1.5 hex bolts suitable for high-pressure applications?
A: Yes, M14x1.5 hex bolts’ finer threads provide better vibration resistance and sealing, making them ideal for high-pressure or precision machinery.
Q: How do I choose between M14 and M13 hex bolts for automotive repairs?
A: Follow the manufacturer’s specifications for thread size and strength. M14 is common for suspension components, while M13 may be used in specific engine parts.
Post time: เม.ย. . 24, 2025 15:24