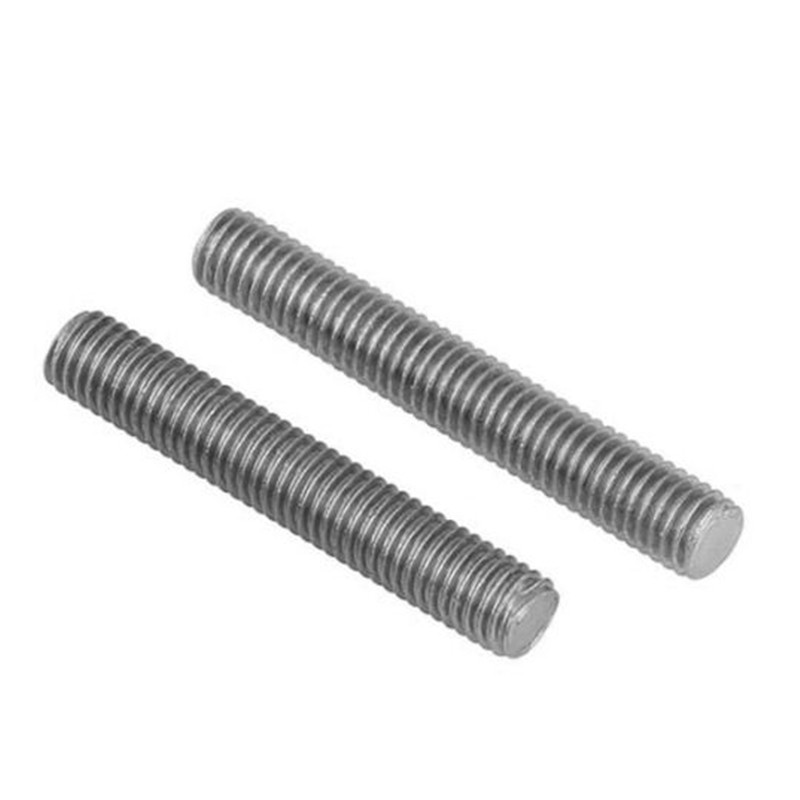
The DIN975 threaded rod standard specifies critical requirements for metric threaded rods used in construction and industrial applications across Europe. When selecting materials for DIN975 compliant products, engineers must consider mechanical properties, environmental factors, and application-specific demands. The high-strength DIN 975 10.9 grade represents one of the most demanding specifications within this standard, requiring careful material selection and heat treatment processes. Understanding the metallurgical options for DIN975 threaded rod enables optimal performance in various loading conditions and operating environments. From standard carbon steel to specialized alloy compositions, the material choice for DIN975 products directly impacts tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and fatigue life. The DIN 975 10.9 classification particularly demands premium materials capable of withstanding significant stress while maintaining thread integrity under vibration and dynamic loads.

Standard Materials for DIN975 Threaded Rod Production
The manufacture of DIN975 compliant threaded rods typically begins with carbon steel as the base material, with specific chemical compositions tailored to meet different property classes. For general-purpose DIN975 threaded rod, manufacturers often use C35 or C45 medium carbon steels that provide adequate strength for most construction applications. The production of DIN 975 10.9 grade rods requires higher quality alloy steels such as 34CrMo4 or 42CrMo4 that can achieve the specified 1000 MPa minimum tensile strength after proper heat treatment. The material selection for DIN975 threaded rod must account for machinability during thread rolling operations while still achieving final mechanical properties. Cold-drawing processes used in manufacturing DIN975 rods enhance the material's yield strength and surface finish, particularly important for the precision threads specified in the standard. For corrosion-resistant applications, DIN 975 10.9 rods may be manufactured from stainless steel grades like A2 (304) or A4 (316), though these require different processing parameters to achieve the necessary mechanical properties while maintaining corrosion resistance.
Heat Treatment Requirements for DIN 975 10.9 درجة
Achieving the stringent mechanical properties of DIN 975 10.9 threaded rods demands precise heat treatment protocols that vary by base material composition. The manufacturing process for high-strength DIN975 threaded rod typically involves quenching and tempering to develop the required microstructure that balances hardness with toughness. For alloy steel DIN975 rods, the quenching process rapidly cools the heated steel to form martensite, followed by tempering to reduce brittleness while maintaining high tensile strength. The DIN 975 10.9 specification requires careful control of tempering temperatures to achieve the perfect balance between strength (minimum 1040 MPa tensile) and ductility (minimum 9% elongation). Induction hardening represents an alternative heat treatment method for DIN975 threaded rod that provides localized hardening of the threaded areas while maintaining toughness in the core material. Post-heat treatment testing of DIN975 products verifies hardness uniformity across the rod length and confirms the absence of excessive decarburization that could compromise thread strength. The DIN 975 10.9 grade additionally requires proof load testing to demonstrate the material's ability to withstand specified stresses without permanent deformation.
Corrosion Protection Options for DIN975 Threaded Rod
Various surface treatments enhance the durability of DIN975 threaded rod in corrosive environments while maintaining compliance with dimensional tolerances. Hot-dip galvanizing represents the most robust corrosion protection for carbon steel DIN975 rods, providing a thick zinc coating that offers sacrificial protection even when scratched. Electroplated zinc coatings offer a more precise but thinner protective layer suitable for DIN 975 10.9 rods where thread dimensions are critical. Manufacturers of DIN975 threaded rod may apply zinc flake coatings that provide excellent corrosion resistance without hydrogen embrittlement risks associated with traditional electroplating. For stainless steel DIN975 variants, passivation treatments enhance the natural oxide layer's protective properties without adding measurable thickness to the threads. The selection of corrosion protection for DIN 975 10.9 rods must consider the intended service environment - coastal applications may require duplex coating systems while industrial atmospheres might need chemical-resistant topcoats. Proper surface preparation before coating application ensures optimal adhesion and performance of protective systems on DIN975 threaded rod, with abrasive blasting being common for heavy coatings like hot-dip galvanizing.
Quality Control and Testing for DIN975 Compliance
Verifying compliance with DIN975 threaded rod specifications requires comprehensive quality control measures throughout the manufacturing process. Dimensional inspections of DIN975 products must confirm thread pitch, major diameter, and thread form conformity to ISO metric thread standards using calibrated ring gauges and optical comparators. Mechanical testing of DIN 975 10.9 rods includes tensile tests to verify yield strength, tensile strength, and elongation meet the 10.9 property class requirements. Hardness testing across multiple points on DIN975 threaded rod ensures uniform heat treatment response, with Rockwell C scale being typical for high-strength grades. Metallurgical examination of DIN975 samples verifies proper microstructure development and absence of defects that could compromise performance in service. For coated DIN 975 10.9 rods, additional tests measure coating thickness, adhesion, and corrosion resistance according to relevant ISO standards. Batch traceability systems document all production parameters and test results for each lot of DIN975 threaded rod, enabling complete quality history retrieval if needed for critical applications.
DIN975 Threaded Rod الأسئلة الشائعة
What Distinguishes DIN 975 10.9 from Other Property Classes?
The DIN 975 10.9 classification specifies minimum 1040 MPa tensile strength and 940 MPa yield strength, significantly higher than property class 8.8 or lower grades in the DIN975 standard.
Can Stainless Steel Achieve DIN 975 10.9 Mechanical Properties?
Certain precipitation-hardening stainless steels can meet DIN975 10.9 requirements, though standard austenitic grades like 304 typically cannot achieve this strength level without compromising corrosion resistance.
How Does DIN975 Threaded Rod Compare to ASTM Equivalents?
DIN975 metric threaded rods are dimensionally incompatible with UNC/UNF threads, while DIN 975 10.9 roughly corresponds to ASTM A193 B7 in tensile strength but with different chemical composition requirements.
What Applications Typically Require DIN 975 10.9 Rods?
High-stress applications like structural steel connections, heavy machinery, and vibration-prone installations commonly specify DIN975 threaded rod in 10.9 grade for its superior strength and fatigue resistance.
How Should DIN975 Rods Be Stored to Maintain Quality?
DIN975 threaded rod should be stored horizontally on racks in dry conditions, with protective end caps to prevent thread damage, and segregated by grade/material to avoid mixing DIN 975 10.9 with lower-strength rods.
For premium quality DIN975 threaded rod in all property classes including DIN 975 10.9, visit our website to explore our certified product range. Our technical team can guide you in selecting the optimal material grade and surface treatment for your specific application requirements. Contact us today to request DIN975 compliance documentation and material test reports, and discover how our precision-manufactured threaded rods can enhance the reliability and safety of your projects. Let us demonstrate why engineers across Europe trust our DIN975 threaded rod solutions for their most demanding structural and mechanical applications.
Post time: أغسطس . 07, 2025 11:06