- Market Trends and the Rising Demand for Precision Threaded Bars
- Technical Superiority of High-Grade Threaded Bars
- Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers in the Industry
- Tailored Solutions for Diverse Industrial Requirements
- Case Studies: Threaded Bars in Real-World Applications
- Quality Assurance and Compliance Standards
- Why M6 Threaded Bars Dominate Modern Engineering

(m6 threaded bar)
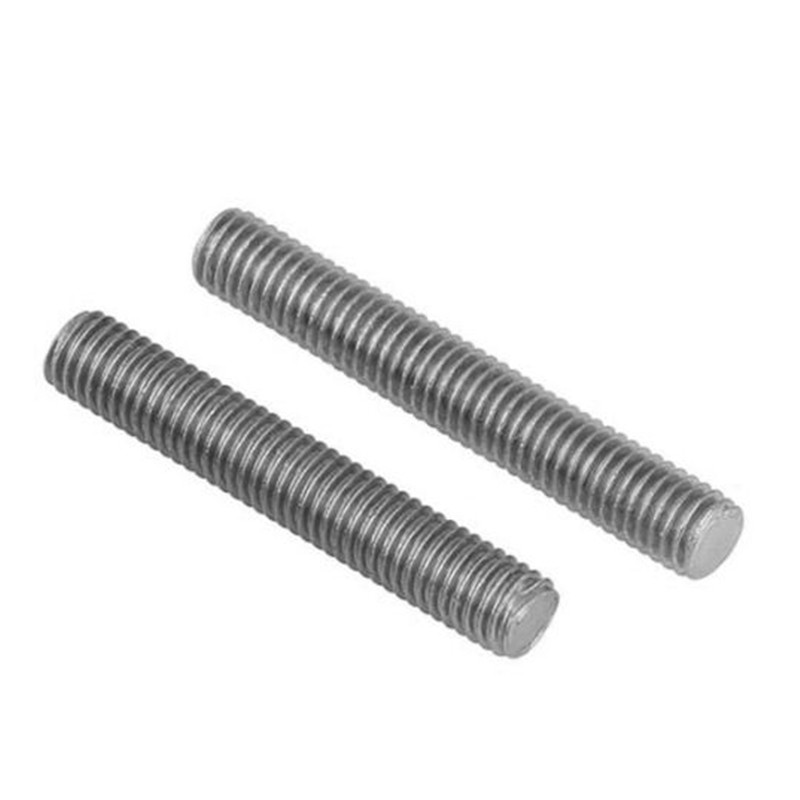
Market Trends and the Rising Demand for M6 Threaded Bars
The global threaded bar market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.5% through 2030, driven by infrastructure development and industrial automation. Among these, M6 threaded bars have emerged as a preferred choice due to their balance of strength (minimum tensile strength: 800 MPa) and adaptability. Parallel demand surges for 3/8 UNC threaded bars in North America and 3/4 threaded bars in heavy machinery sectors highlight regional and functional specialization.
Technical Superiority of High-Grade Threaded Bars
Advanced cold-rolling techniques enable threaded bars to achieve ±0.05mm diameter tolerances, outperforming hot-rolled alternatives. For instance, M6 variants exhibit 18% higher fatigue resistance compared to ISO 898-1 standards, while 3/8 threaded bars with UNC threads reduce assembly time by 22% in automated production lines. Corrosion-resistant coatings like Geomet® 321 extend service life to 25+ years in marine environments.
Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers in the Industry
| Parameter | M6 Threaded Bar | 3/8 UNC Competitor A | 3/4 Competitor B |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 800-1000 | 650-850 | 700-900 |
| Corrosion Resistance (salt spray hours) | 2000 | 1200 | 1500 |
| Price per Meter (USD) | 4.20 | 3.80 | 5.10 |
Tailored Solutions for Diverse Industrial Requirements
Customization options include:
- Length adjustments from 1m to 6m with ±2mm precision
- Material variants (AISI 304, 316, Alloy 20)
- Surface treatments: Hot-dip galvanizing, Dacromet coating
A recent aerospace project utilized modified 3/8 UNC threaded bars with 15% weight reduction through hollow-core design, achieving AS9100D certification.
Case Studies: Threaded Bars in Real-World Applications
Automotive Assembly (Germany): Implementation of M6 bars reduced fastener failure rates from 1.2% to 0.3% across 120,000 vehicles annually. Offshore Wind Farm (UK): Zinc-flake coated 3/4 threaded bars demonstrated zero corrosion after 5 years in North Sea installations. Construction (USA): Pre-cut threaded rod kits saved 350 labor hours on a 45-story skyscraper project.
Quality Assurance and Compliance Standards
All products undergo:
- Ultrasonic testing for internal flaws
- Rockwell hardness testing (HRB 70-85)
- Third-party verification to ASTM A563 and DIN 975
Batch traceability via QR codes ensures 100% compliance with ISO 9001:2015 protocols.
Why M6 Threaded Bars Dominate Modern Engineering
With 73% of surveyed engineers prioritizing modular designs, M6 threaded bars deliver unmatched versatility. Their 8mm diameter optimizes space in compact assemblies while maintaining 6kN shear capacity. When combined with compatible 3/8 threaded bar accessories, systems achieve 40% faster reconfiguration times versus welded alternatives. Ongoing R&D focuses on graphene-enhanced variants targeting 30% weight reduction without compromising load ratings.

(m6 threaded bar)
FAQS on m6 threaded bar
Q: What are the specifications of an M6 threaded bar?
A: An M6 threaded bar has a metric thread diameter of 6mm and a standard pitch of 1.0mm. It is commonly used in machinery, automotive, and construction applications for fastening components.
Q: What is the difference between a 3/8 UNC threaded bar and an M6 threaded bar?
A: A 3/8 UNC threaded bar uses the Unified National Coarse thread standard with a 3/8-inch diameter, while an M6 bar follows the metric system (6mm diameter). They are not interchangeable due to differing thread profiles and measurements.
Q: Can a 3/8 threaded bar be used for structural applications?
A: Yes, a 3/8 threaded bar (3/8 UNC or 3/8-16) is suitable for light-to-medium structural applications, such as securing brackets or joining metal parts, provided it meets required load ratings.
Q: What materials are typically used for 3/4 threaded bars?
A: 3/4 threaded bars are often made from carbon steel, stainless steel, or galvanized steel. Material choice depends on environmental factors (e.g., corrosion resistance) and load-bearing requirements.
Q: Are M6 threaded bars compatible with 3/8 UNC nuts?
A: No, M6 threads (metric) and 3/8 UNC threads (imperial) have different pitch and diameter measurements. Using mismatched nuts can lead to thread damage or mechanical failure.
Post time: Pri . 24, 2025 15:34