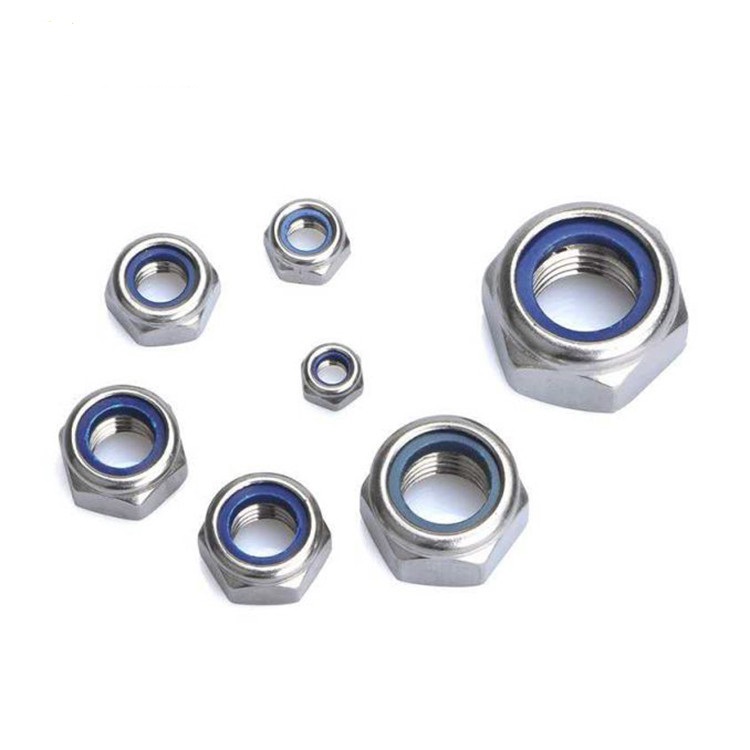
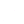
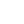
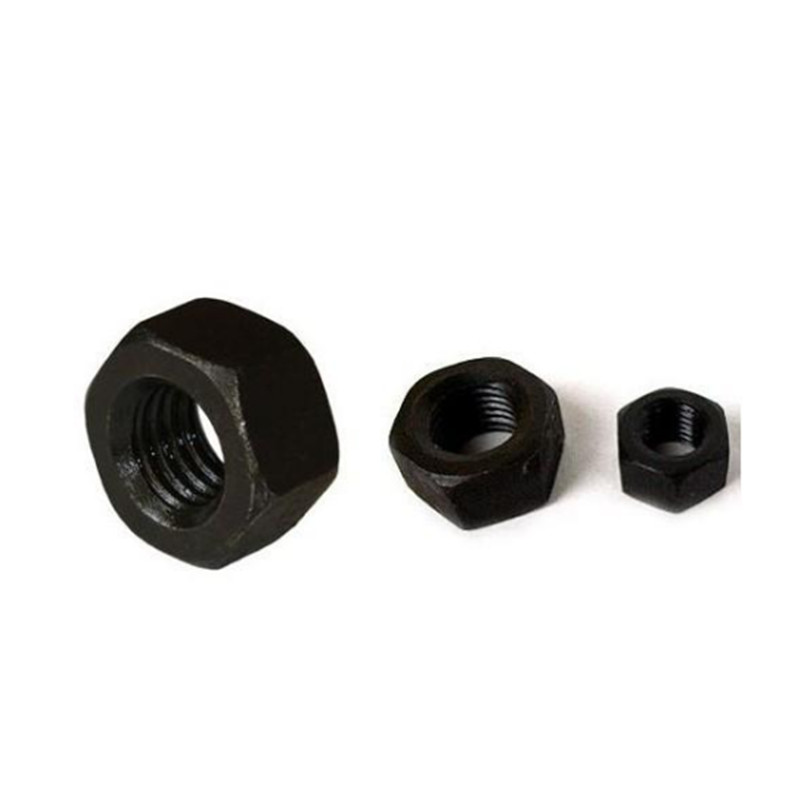
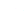In the demanding world of industrial applications, where structural integrity and longevity are paramount, the choice of fasteners plays a critical role. Among the myriad options available, the galvanized hex nut stands out as a superior solution, particularly the DIN934 Hex Nut, renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance and robust performance. This comprehensive guide delves into the specifics of these vital components, exploring their market trends, technical prowess, manufacturing intricacies, and diverse applications, while underscoring their pivotal role in modern engineering.
Industry Trends and the Evolving Demand for Durable Fasteners
The global fastener market is experiencing robust growth, driven by expansion in key sectors such as construction, automotive, aerospace, and renewable energy. A significant trend within this market is the escalating demand for high-performance fasteners that offer superior durability and resistance to environmental degradation. Industries are increasingly moving towards materials and coatings that extend product lifespan, reduce maintenance costs, and enhance safety. This paradigm shift directly benefits products like the galvanized hex nut, which provides excellent protection against corrosion, a leading cause of structural failure and increased operational expenses.
According to a report by Grand View Research, the global industrial fasteners market size was valued at USD 90.71 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.5% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is largely attributable to infrastructure development projects, the automotive industry's electrification trend, and the burgeoning renewable energy sector, all of which require reliable and long-lasting fastening solutions. The emphasis on sustainability and circular economy principles also favors galvanized hex nuts, as zinc coatings are recyclable and contribute to extended asset life, reducing waste and resource consumption.
Technical Parameters and Specifications of DIN934 Hex Nut
The DIN934 Hex Nut is a standard hexagonal nut widely used in conjunction with bolts, screws, and washers to fasten mechanical parts together. Its design ensures a secure and strong connection, crucial for various applications. When galvanized, its utility extends to harsh environments where corrosion is a major concern.
Material Composition and Mechanical Properties
Typically, DIN934 Hex Nuts are manufactured from high-quality steel, commonly carbon steel hex nuts (e.g., Grade 2, 5, 8, 10, 12 per ASTM F568M or ISO 898-1 standards) or stainless steel (e.g., A2, A4 grades). The choice of base material dictates the mechanical properties such as tensile strength, proof load, and hardness. For instance, an 8.8 grade carbon steel nut paired with an 8.8 grade bolt offers a robust connection capable of withstanding significant stress.
The galvanization process, either hot-dip galvanizing (HDG) or electro-galvanizing, applies a protective zinc coating. Hot-dip galvanizing, conforming to standards like ASTM A153/A153M or ISO 1461, provides a thick, durable coating of zinc-iron alloy layers that offers sacrificial and barrier protection against corrosion. Electro-galvanizing (or zinc plating) provides a thinner, aesthetically pleasing finish, typically compliant with ASTM B633. For structural applications in outdoor or corrosive environments, HDG is preferred for its superior long-term protection compared to plain carbon steel hex nuts or black hex nuts (which often have a black oxide finish offering minimal corrosion resistance).
Key Dimensions and Tolerances
The galvanized hex nut (DIN934) adheres to strict dimensional standards ensuring interchangeability and proper fit. Key parameters include thread size (M), pitch, width across flats (s), and thickness (m).
| Nominal Thread Diameter (M) | Thread Pitch (P) (mm) | Width Across Flats (s) (mm) | Nominal Height (m) (mm) | Common Material Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M6 | 1.0 | 10 | 5.0 | Class 8 / A2 |
| M8 | 1.25 | 13 | 6.5 | Class 8 / A2 |
| M10 | 1.5 | 17 | 8.0 | Class 8 / A4 |
| M12 | 1.75 | 19 | 10.0 | Class 10 / A4 |
| M16 | 2.0 | 24 | 13.0 | Class 10 / A4 |
| M20 | 2.5 | 30 | 16.0 | Class 10 / A4 |
| M24 | 3.0 | 36 | 19.0 | Class 10 / A4 |
| M30 | 3.5 | 46 | 24.0 | Class 10 / A4 |
It is critical to note that for hot-dip galvanized nuts, the internal threads are often tapped oversized after galvanizing to accommodate the thickness of the zinc coating on the mating bolt, ensuring a proper fit and preventing thread stripping. This practice complies with standards like ASTM A563, which specifies requirements for nuts used with hot-dip galvanized fasteners.

Unveiling the Manufacturing Process of Galvanized Hex Nuts
The production of a high-quality galvanized hex nut is a sophisticated process that combines precision engineering with material science expertise. The entire journey, from raw material to finished product, is meticulously controlled to ensure adherence to international standards and superior performance.
Detailed Manufacturing Flow for DIN934 Hex Nut
-
1
Wire Rod Preparation and Drawing
High-quality steel wire rods, often of specific carbon content for desired mechanical properties, are cleaned and descaled. These rods then undergo a cold drawing process to reduce their diameter to the precise size required for the nut blank. This cold working also enhances the material's strength and surface finish.
-
2
Cold Heading/Cold Forming
The drawn wire is fed into multi-station cold heading machines. Through a series of high-pressure strokes, the wire is cut into blanks, and these blanks are then cold-formed into the approximate hexagonal shape of the nut, along with a central hole. Cold forming is preferred for its efficiency, material savings, and ability to improve grain structure, leading to stronger nuts.
-
3
Tapping (Internal Threading)
The pre-formed blanks are then transferred to tapping machines. Here, the internal threads are precisely cut into the central hole using high-speed taps. For galvanized hex nuts, especially those destined for hot-dip galvanizing, the threads are often tapped oversized (e.g., class 2B for UNC/UNF threads or 6AZ for metric threads) to accommodate the zinc coating thickness that will be applied later. This critical step ensures proper fit with galvanized bolts without damaging the coating.
-
4
Heat Treatment (if required)
Depending on the required strength class (e.g., Class 8, 10, 12), nuts undergo heat treatment processes such as quenching and tempering. This involves heating the nuts to a specific temperature and then rapidly cooling them (quenching) followed by reheating to a lower temperature (tempering). This process refines the microstructure, increasing the nut's hardness, tensile strength, and fatigue resistance.
-
5
Surface Treatment: Galvanization
This is the defining step for galvanized hex nuts. The nuts are thoroughly cleaned (degreasing, pickling in acid to remove scale and rust, rinsing, and fluxing to prepare the surface for zinc adhesion).
Hot-Dip Galvanizing: Nuts are immersed in a bath of molten zinc (typically at 450°C). The iron in the steel reacts with the molten zinc to form a series of intermetallic alloy layers and an outer layer of pure zinc. This provides a robust, metallurgical bond offering cathodic (sacrificial) protection and a physical barrier.
Electro-Galvanizing (Zinc Plating): Nuts are immersed in an electrolytic solution containing zinc ions. An electric current causes the zinc ions to deposit onto the nut's surface, forming a thin, uniform coating. This method offers a smoother finish but less corrosion resistance than HDG. For DIN934 Hex Nuts used in outdoor structural applications, HDG is generally specified. -
6
Post-Galvanization Treatment (Hydrogen Embrittlement Relief)
For high-strength nuts (typically Class 10.9 and above for bolts, and corresponding nuts), there is a risk of hydrogen embrittlement during acid pickling or electroplating. To mitigate this, a baking process (often at 200°C for several hours) is performed immediately after plating or pickling to drive out hydrogen atoms trapped in the steel microstructure, preventing delayed brittle fracture.
-
7
Quality Control and Inspection
Throughout the manufacturing process, rigorous quality control measures are implemented. This includes dimensional checks, thread gauge checks, visual inspection for defects, and mechanical property testing (hardness, proof load, tensile strength for mating bolts). For galvanized nuts, coating thickness, adhesion, and uniformity are also tested according to relevant standards like ISO 1461, ASTM A153/A153M. These inspections ensure the DIN934 Hex Nut meets all specified requirements for quality, performance, and safety.
-
8
Packaging and Dispatch
Once approved, the galvanized hex nutes are counted, packaged securely, and labeled for dispatch. Proper packaging protects the nuts during transit and storage, preventing damage to the zinc coating.
The meticulous adherence to these steps and international standards like ISO, ANSI, ASTM ensures that each galvanized hex nut delivers optimal performance and a long service life, typically far exceeding that of untreated fasteners. For instance, in an industrial marine environment, a hot-dip galvanized coating on a DIN934 Hex Nut can provide protection for 50 years or more, significantly reducing the lifecycle costs associated with corrosion.
Diverse Application Scenarios and Enduring Advantages
The robust properties of the galvanized hex nut make it an indispensable component across a multitude of industries, particularly where exposure to harsh environmental conditions is a concern.
Key Applicable Industries:
- Construction & Infrastructure: From bridges and highways to commercial buildings and stadiums, galvanized hex nuts are critical for structural steel connections, ensuring long-term stability and resistance to weathering. Their use in outdoor structures like guardrails, scaffolding, and public utility poles is widespread due to superior corrosion protection.
- Energy Sector (Oil & Gas, Renewables): In petrochemical plants, offshore oil rigs, wind turbines, and solar farms, fasteners are subjected to extreme conditions including chemical exposure, high humidity, and corrosive salts. Galvanized hex nuts (including those used in black oxide hex bolts and nuts assemblies for specific aesthetic or frictional requirements) provide the necessary resilience to prevent premature failure and ensure operational continuity, thereby contributing to significant energy savings by preventing system downtime.
- Metallurgy & Mining: Equipment used in these sectors often operates in abrasive and corrosive environments. Fasteners must withstand constant wear and tear. Galvanized nuts and bolts ensure the integrity of heavy machinery, conveyor systems, and processing equipment.
- Water & Wastewater Treatment: Facilities dealing with water and chemical processes are inherently prone to corrosion. Galvanized hex nuts are ideal for pipe flange connections, pump installations, and structural elements within treatment plants, offering exceptional resistance to moisture and chemical agents.
- Marine & Shipbuilding: Exposure to saltwater is one of the most aggressive corrosive environments. Fasteners on ships, docks, and offshore platforms demand the highest level of corrosion protection, making hot-dip galvanized hex nuts a standard choice.
- Agriculture: Farm machinery, fencing, and barn structures are exposed to weather, chemicals, and animal waste. Galvanized fasteners offer the durability needed for these demanding agricultural applications.
Distinct Technical Advantages:
- Superior Corrosion Resistance: Hot-dip galvanizing provides a thick, metallurgically bonded zinc coating that acts as both a barrier and offers cathodic protection. This means even if the coating is scratched, the surrounding zinc sacrifices itself to protect the underlying steel, significantly extending the lifespan compared to a simple black hex nut or a painted carbon steel fastener. This anti-corrosion property is crucial for the longevity of infrastructure, preventing costly early replacements.
- Extended Service Life & Reduced Maintenance: Due to their exceptional corrosion resistance, galvanized hex nuts require less frequent replacement and maintenance. This translates into substantial long-term cost savings, reduced downtime for equipment, and improved operational efficiency. For example, a study by the American Galvanizers Association found that galvanized steel can last 70 years or more in many environments without maintenance.
- Durability and Strength: The galvanization process does not compromise the inherent strength of the base steel. When produced to standards like DIN934, these nuts retain their mechanical properties while gaining superior corrosion protection, making them ideal for high-stress applications.
- Cost-Effectiveness Over Lifecycle: While the initial cost of a galvanized hex nut might be slightly higher than an untreated one, the total lifecycle cost is significantly lower due to reduced maintenance, repair, and replacement needs. This long-term value proposition is a major driver for their adoption in critical applications.
- Environmental Benefits: Zinc is a naturally abundant, recyclable material. The use of galvanized fasteners supports sustainable practices by extending product life and reducing the overall material consumption and waste generated from frequent replacements.

Choosing the Right Manufacturer: Expertise, Experience, and Authoritativeness
When sourcing critical components like galvanized hex nuts, selecting a reputable and experienced manufacturer is paramount. A company's expertise, proven track record, and authoritative standing in the industry directly impact the quality, reliability, and ultimately, the safety of your projects.
Key Criteria for Manufacturer Comparison:
- Certifications & Quality Management: A leading manufacturer should possess international quality certifications such as ISO 9001:2015, which demonstrates a robust quality management system covering design, development, production, installation, and servicing. Certification for specific product standards (e.g., adherence to ASTM, ANSI, DIN, ISO for fasteners) is also crucial.
- Material Traceability: The ability to trace raw materials back to their origin ensures consistent quality and compliance with industry standards. Reputable manufacturers maintain stringent records of material batches, chemical compositions, and mechanical test results.
- Production Capacity & Technology: Modern manufacturing facilities equipped with advanced cold heading machines, precision tapping equipment, state-of-the-art heat treatment furnaces, and controlled galvanizing lines indicate a manufacturer's capability to produce high volumes of consistent quality fasteners.
- R&D and Customization Capabilities: A forward-thinking manufacturer invests in research and development to improve product performance and offer innovative solutions. The ability to provide customized solutions – such as non-standard sizes, unique coatings, or specific material grades – showcases adaptability to diverse client needs.
- Customer Service & Technical Support: Excellent pre-sales consultation, responsive customer support, and expert technical assistance for installation and application queries are hallmarks of a trustworthy partner.
- Industry Experience & Reputation: A manufacturer with decades of service in the fastener industry, positive client testimonials, and a strong market presence (like the provider of DIN934 Hex Nuts on hbtbls.com) demonstrates deep understanding and reliability. Our company, with over two decades of dedicated service in fastener manufacturing and supply, stands as a testament to our commitment to quality and client satisfaction.
Tailored Customization Solutions for Unique Project Demands
Recognizing that standard products may not always meet every project's unique specifications, reputable manufacturers offer comprehensive customization solutions for galvanized hex nuts and other fasteners. This flexibility is vital for specialized industries or applications with specific performance requirements.
Customization can encompass:
- Non-Standard Dimensions: Production of nuts with unique thread sizes, widths across flats, or heights not covered by standard DIN934 or other international norms.
- Special Materials: Use of specific alloys beyond standard carbon steel or stainless steel, such as high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steels or specific corrosion-resistant alloys, for enhanced performance in extreme conditions.
- Advanced Coatings: Application of specialized coatings in addition to or instead of standard galvanization, such as fluoropolymer coatings for chemical resistance, zinc-nickel coatings for enhanced corrosion performance, or ceramic coatings for high-temperature applications. This is especially relevant when considering alternatives to, or complementing, standard black oxide hex bolts and nuts for particular environments.
- Specific Testing Protocols: Conducting additional non-destructive testing (NDT) like magnetic particle inspection, ultrasonic testing, or eddy current testing, or specific mechanical tests beyond standard requirements, such as fatigue testing or salt spray testing, to meet stringent project specifications.
- Batch Identification & Traceability: Enhanced marking or coding for individual nuts or batches to improve traceability for critical applications.
- Packaging Solutions: Customized packaging to protect fasteners during shipping, facilitate easier handling on-site, or comply with specific project logistics.
The process of developing a customized galvanized hex nut solution typically involves close collaboration between the client and the manufacturer's engineering team, ensuring that the final product precisely matches the application's demands while maintaining cost-effectiveness and timely delivery.
Real-World Impact: Application Cases and Success Stories
The practical utility and long-term benefits of galvanized hex nuts are best illustrated through their successful deployment in real-world projects. These examples underscore the tangible advantages of choosing high-quality, corrosion-resistant fasteners.
Case Study 1: Coastal Bridge Construction (Infrastructure)
A major bridge project located in a highly corrosive coastal environment required fasteners capable of withstanding constant exposure to saltwater spray and high humidity. Standard carbon steel hex nuts would rapidly corrode, leading to structural integrity issues and significant maintenance costs. The solution involved utilizing thousands of hot-dip galvanized hex nuts, specifically DIN934 Hex Nuts (Grade 8.8, oversized tapped).
Outcome: After five years, detailed inspections revealed no signs of significant corrosion on the galvanized fasteners, performing far superior to the expected lifespan of non-galvanized alternatives. This eliminated the need for costly early replacements and repainting, contributing to significant budget savings and enhanced safety. Engineers cited the robust intermetallic layers formed during hot-dip galvanizing as key to its longevity.
Case Study 2: Offshore Wind Turbine Installation (Renewable Energy)
For an offshore wind farm, the immense forces on the turbine structures and the aggressive marine environment demanded fasteners with extreme durability. The project specified high-strength (Class 10.9) galvanized hex nuts, conforming to DIN934 and ASTM A153 standards, for critical tower and blade connections.
Outcome: The hot-dip galvanized nuts successfully resisted corrosion from saltwater and atmospheric conditions, ensuring the structural integrity of the turbines over their projected 25-year lifespan. The client reported minimal fastener-related failures, directly contributing to consistent energy generation and proving the cost-effectiveness of investing in high-quality corrosion protection. This also allowed for optimized maintenance schedules, reducing the need for dangerous and costly offshore repairs.
Case Study 3: Wastewater Treatment Plant Expansion (Water Treatment)
An expansion of a municipal wastewater treatment plant involved numerous pipe connections, tank assemblies, and structural supports, all exposed to corrosive chemicals and high humidity. The previous phase of the plant had faced significant issues with fastener corrosion using standard plain finish bolts and nuts. For the expansion, hot-dip galvanized hex nuts were specified throughout.
Outcome: The galvanized fasteners exhibited excellent resistance to the harsh chemical environment. Facility engineers noted a drastic reduction in corrosion-related fastener failures, leading to safer operations, reduced leakage points, and an overall improvement in the plant's operational efficiency and environmental compliance. The long service life of the galvanized fasteners significantly reduced the plant’s operational expenditure on maintenance and replacement parts.
Trustworthiness: Assurance through Quality, Delivery, and Support
Establishing trust with clients is paramount. This is achieved not just through product quality but also via transparent processes, reliable service, and robust support systems.
- Delivery Cycle: We prioritize efficient logistics and supply chain management to ensure timely delivery. For standard galvanized hex nuts, typical lead times range from 3-5 business days for stock items, and 2-4 weeks for custom orders or bulk production, depending on complexity and volume. We provide clear, upfront delivery estimates and track shipments meticulously.
- Quality Assurance & Warranty: All our DIN934 Hex Nuts, especially our galvanized hex nutes, undergo stringent multi-stage quality control as per ISO 9001:2015. We offer a comprehensive warranty against manufacturing defects, guaranteeing product performance under specified conditions. Our products meet or exceed relevant international standards like ASTM, ANSI, and ISO.
- Customer Support: Our dedicated customer support team is available via phone, email, and online chat to assist with inquiries, technical specifications, order tracking, and after-sales support. We provide detailed product documentation, installation guides, and offer expert advice to ensure optimal application of our fasteners.
Professional FAQ for Galvanized Hex Nuts
1. What is the primary difference between a galvanized hex nut and a standard carbon steel hex nut?
The primary difference lies in corrosion resistance. A standard carbon steel hex nut is susceptible to rust and corrosion, especially in moist or corrosive environments. A galvanized hex nut has a protective zinc coating applied through processes like hot-dip galvanizing or electro-galvanizing. This zinc layer provides a barrier against corrosive elements and offers sacrificial protection, significantly extending the nut's lifespan and performance in harsh conditions.
2. How does hot-dip galvanizing protect a galvanized hex nut from corrosion?
Hot-dip galvanizing protects in two ways: as a barrier coating and through cathodic protection. The zinc coating physically separates the steel from the corrosive environment. Additionally, zinc is more electrochemically active than steel. If the coating is scratched, the zinc sacrifices itself (corrodes) preferentially to protect the underlying steel, preventing rust from forming at the damaged area. This is a significant advantage over passive coatings like paint or black oxide hex bolts and nuts finishes.
3. What is DIN934 standard for hex nuts?
DIN934 is a German industrial standard that specifies the dimensions, tolerances, and mechanical properties for common hexagonal nuts. It ensures interchangeability and compatibility of nuts with corresponding bolts and washers globally. Our DIN934 Hex Nuts adhere strictly to these specifications for reliable performance.
4. Are there special considerations for installing galvanized hex nuts with bolts?
Yes. For hot-dip galvanized hex nuts, the internal threads are often tapped oversized after the galvanizing process to accommodate the zinc coating thickness on the mating galvanized bolt threads. This ensures a proper, interference-free fit and prevents thread damage. Always use galvanized nuts with galvanized bolts of the same coating type and mechanical properties, and consider using a lubricant on the bolt threads to prevent galling during tightening.
5. What is the typical lifespan of a galvanized hex nut in outdoor environments?
The lifespan of a galvanized hex nut varies significantly depending on the environment. In rural environments, it can last 70 years or more. In typical urban or industrial environments, 30-50 years is common. In severe marine or highly corrosive chemical environments, the lifespan might be reduced to 10-25 years, but this is still significantly longer than untreated fasteners. The zinc coating's thickness is a primary determinant of lifespan.
6. Can galvanized hex nuts be used with black oxide hex bolts and nuts?
While technically possible, it is generally not recommended for long-term outdoor or corrosive applications due to dissimilar corrosion protection properties. A black oxide hex bolts and nuts assembly primarily provides a black aesthetic and very minimal corrosion resistance, mainly for indoor, dry environments. Combining it with a galvanized hex nut means the nut will outperform the bolt in corrosion resistance, potentially leading to premature failure of the bolt. For optimal performance and uniform corrosion protection, use fasteners with matching finishes (e.g., all galvanized or all black oxide if suitable for the environment).
7. What inspection standards should a high-quality galvanized hex nut meet?
High-quality galvanized hex nuts should meet several key standards. For mechanical properties, ISO 898-2 or ASTM A563 are crucial. For hot-dip galvanizing, ASTM A153/A153M (for individual pieces like nuts) or ISO 1461 (for general galvanized coatings) are the primary standards, covering coating thickness, adhesion, and uniformity. Adherence to DIN934 ensures dimensional accuracy. Reputable manufacturers also often have ISO 9001 quality management system certification.
This article draws upon established industry standards and research. For further reading on galvanizing, consult resources such as the American Galvanizers Association (galvanizeit.org) and the Galvanizers Association UK (galvanizing.org.uk). Information on fastener standards can be found from organizations like ASTM International (astm.org) and the International Organization for Standardization (iso.org).
Post time: Aug . 08, 2025 07:20