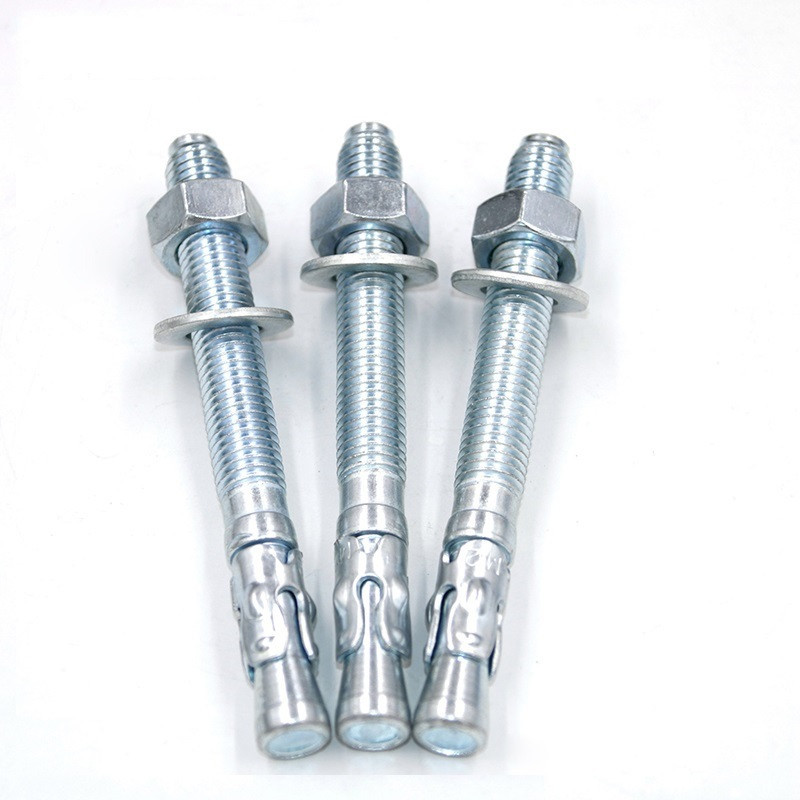
The Unseen Strength: Unlocking the Potential of Galvanized Hex Nut Technology
In the vast landscape of industrial fasteners, the **galvanized hex nut** stands out as a critical component, underpinning structural integrity and operational reliability across countless sectors. Far more than just a threaded piece of metal, a high-quality **galvanized hex nut** represents a sophisticated blend of material science, precision engineering, and advanced protective coatings. This deep dive explores the multifaceted world of these essential fasteners, focusing on their evolving role, technical nuances, and the unparalleled advantages they offer in demanding environments.
Industry Trends and the Growing Demand for Corrosion Resistance
The global industrial fasteners market is experiencing robust growth, driven by expansion in manufacturing, infrastructure development, and renewable energy sectors. A significant trend within this market is the escalating demand for fasteners with superior corrosion resistance. This is particularly true for applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions, such as outdoor construction, marine environments, chemical processing plants, and urban infrastructure where atmospheric corrosion is a constant threat.
According to a report by Grand View Research, the global fasteners market size was valued at USD 86.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.5% from 2023 to 2030. Within this, the demand for coated fasteners, including **galvanized hex nuts**, is projected to outpace the general market due to stricter safety regulations, increased focus on long-term asset integrity, and the rising cost of maintenance and replacement associated with corroded components.
The emphasis on sustainability and extended service life also plays a crucial role. Industries are moving towards components that minimize waste and energy consumption over their lifecycle. A **galvanized hex nut**, with its extended lifespan, significantly contributes to reducing the environmental footprint by decreasing the frequency of replacement and associated material and energy costs. Furthermore, the push towards green infrastructure, such as wind farms and solar installations, inherently requires fasteners that can withstand decades of outdoor exposure, making galvanization a preferred solution.
Understanding the DIN934 Hex Nut: Specifications and Parameters
At the heart of the **galvanized hex nut** discussion lies the DIN934 standard, which dictates the dimensions, tolerances, and mechanical properties of hex nuts for general use. The DIN934 Hex Nut is widely recognized and adopted globally, ensuring interchangeability and reliability across different applications.
Expertise The core material for a standard **carbon steel hex nut** conforming to DIN934 is often carbon steel, which offers an excellent balance of strength and cost-effectiveness. The galvanization process then adds a layer of zinc, providing sacrificial cathodic protection against corrosion.
Key Technical Parameters of Galvanized Hex Nut (DIN934)
To illustrate the typical specifications of a **galvanized hex nut**, consider the following data table:
| Parameter | Description | Typical Range/Value (DIN934) | Significance for Galvanized Nuts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | Deutsches Institut für Normung 934 | DIN934 / ISO 4032 (Equivalent) | Ensures dimensional consistency and interchangeability. |
| Material | Carbon Steel Grade | Steel grades 4, 5, 8, 10 (Property Classes) | Strength and mechanical performance of the base nut. Carbon steel hex nut is common. |
| Coating Type | Hot-Dip Galvanization | ASTM A153 / ISO 10684 | Superior corrosion resistance; specified for durability. |
| Zinc Coating Thickness | Average thickness of zinc layer | ≥ 45-85 µm (micrometers) depending on size | Directly impacts corrosion protection duration. Thicker coating = longer life. |
| Thread Type | Metric Coarse Thread | M3 to M64 (Common sizes) | Standardized for compatibility with metric bolts. Hot-dip galvanized nuts are often tapped oversized after galvanizing to accommodate the coating on the bolt. |
| Proof Load | Maximum load a nut can withstand without permanent deformation | Varies by property class and size (e.g., 800 MPa for Class 8) | Ensures structural integrity under design loads. |
| Hardness | Resistance to indentation | Varies by property class (e.g., Rockwell C 19-30 for Class 8) | Indicates resistance to wear and deformation. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Salt Spray Test (ASTM B117) | 1000+ hours to red rust (typical for HDG) | Quantitative measure of resistance to atmospheric corrosion and chemical exposure. |
| Service Temperature Range | Operating temperature limits | Up to 200°C (392°F) for HDG | Ensures performance stability in various thermal environments. Higher temperatures can affect zinc coating. |
Compared to a standard **black hex nut** or a **black oxide hex bolts and nuts** assembly, the galvanized version offers significantly superior long-term corrosion protection, albeit with a different aesthetic and slightly increased dimensions due to the coating thickness. While black oxide offers some corrosion resistance and an aesthetically pleasing dark finish, it is typically less durable in harsh outdoor or corrosive environments than hot-dip galvanizing.
The Manufacturing Journey: Crafting the Galvanized Hex Nut
Expertise The production of a high-quality **galvanized hex nut** is a sophisticated multi-stage process, combining precise mechanical forming with advanced surface treatment. This intricate journey ensures that the final product meets stringent industry standards for strength, durability, and corrosion resistance.
Detailed Process Flow of Galvanized Hex Nut Manufacturing
-
Material Selection and Preparation:
The process begins with selecting high-grade steel wire rods, typically low to medium **carbon steel hex nut** material (e.g., C1008, C1010, C1018, or higher grades for specific strength requirements). These rods are uncoiled, straightened, and cut into precise lengths, which will form the blanks for the nuts.
-
Cold Forging/Forming (Nut Forming):
This is the primary shaping process. The cut steel blanks are fed into multi-station cold forging machines. Through a series of high-pressure dies, the steel is progressively formed into the characteristic hexagonal shape of the nut. This includes heading (forming the hexagonal head) and punching (creating the central hole). Cold forming enhances the mechanical properties of the steel, increasing its tensile strength and fatigue resistance due to work hardening.
(Imagine a diagram here: Steel Rod -> Cut Blanks -> Multi-station Cold Former -> Hexagonal Nut Blank)
-
Tapping (Thread Rolling/Cutting):
After forming, the internal threads are created. For **DIN934 Hex Nut** specifications, this typically involves tapping the pre-drilled hole. Crucially, for hot-dip galvanizing, the nuts are often tapped oversized *after* the galvanizing process, or a slight overtap is performed beforehand to accommodate the zinc coating thickness on the mating bolt. This ensures proper fit and function without binding, addressing a common challenge with coated fasteners. The thread quality is paramount for load distribution and torque-tension performance.
-
Heat Treatment (Optional but Common):
Depending on the required property class (e.g., Class 8, 10 for high strength), the formed and threaded nuts may undergo heat treatment. This typically involves quenching (heating to a high temperature and rapidly cooling) followed by tempering (reheating to a lower temperature). Heat treatment refines the microstructure, enhancing the nut's mechanical properties like hardness, tensile strength, and impact resistance.
-
Cleaning and Surface Preparation for Galvanization:
Before galvanizing, the nuts must be meticulously cleaned to ensure the zinc can bond properly to the steel. This multi-step process includes:
- Degreasing: Removal of oils, grease, and dirt using alkaline solutions.
- Pickling: Immersion in acidic solutions (hydrochloric or sulfuric acid) to remove rust and mill scale. This step is critical for a clean iron surface.
- Rinsing: Thorough rinsing with water to remove residual acids and salts.
- Fluxing: Immersion in a flux solution (typically zinc ammonium chloride). The flux cleans the surface further and prevents oxidation before immersion in molten zinc, promoting proper wetting and bonding.

-
Hot-Dip Galvanizing:
The cleaned and fluxed nuts are then immersed in a bath of molten zinc, maintained at a temperature of around 450°C (840°F). During this immersion, the iron of the steel reacts metallurgically with the molten zinc to form a series of zinc-iron alloy layers, followed by an outer layer of pure zinc. This forms a robust, metallurgically bonded coating that provides both barrier and cathodic protection.
(Imagine a diagram here: Cleaned Nut -> Molten Zinc Bath -> Metallurgical Bonding -> Coated Nut)
-
Cooling and Quenching:
After removal from the zinc bath, the nuts are cooled. This can be done by air-cooling or quenching in water, depending on the desired finish and potential for distortion. Rapid cooling helps achieve a smoother, brighter finish.
-
Post-Galvanization Treatments (Optional):
Some nuts may undergo chromate passivation post-galvanizing. This chemical treatment enhances the appearance and further delays the formation of white rust (zinc corrosion products) during storage and initial exposure.
-
Quality Control and Inspection:
Rigorous quality control is applied at every stage, but especially after galvanizing. Key inspections for a finished **galvanized hex nut** include:
- Visual Inspection: Checking for uniform coating, absence of bare spots, lumps, or excessively thick areas.
- Coating Thickness Measurement: Using magnetic or eddy current gauges (e.g., according to ASTM E376 or ISO 2178) to ensure the zinc layer meets specified minimums (e.g., as per ASTM A153 or ISO 10684).
- Adhesion Testing: Ensuring the zinc coating is well-bonded to the steel base (e.g., by chisel or knife test for larger parts, or bending tests for specific applications).
- Mechanical Property Testing: Verifying tensile strength, proof load, and hardness to ensure the nut still meets the specified property class requirements after galvanizing.
- Thread Fit Gauging: Using GO/NO-GO gauges to confirm that the oversized tapped threads are within acceptable tolerances for proper mating with galvanized bolts.
This comprehensive process ensures that each galvanized hex nut from reputable manufacturers like HBTBLS not only meets but often exceeds international standards like ISO and ANSI, guaranteeing a long service life and optimal performance in diverse applications.

Application Scenarios and Strategic Advantages
Experience The inherent durability and corrosion resistance of the **galvanized hex nut** make it indispensable across a multitude of heavy-duty and outdoor industrial applications. Its ability to withstand environmental stressors without significant degradation translates directly into enhanced safety, reduced maintenance costs, and extended operational lifespans for critical infrastructure and machinery.
Key Applicable Industries:
- Petrochemical & Oil & Gas: In refineries, offshore platforms, and pipelines, fasteners are exposed to corrosive chemicals, saltwater, and extreme temperatures. **Galvanized hex nuts** are crucial for securing structural components, piping systems, and equipment, ensuring integrity and preventing hazardous leaks or failures. Their anti-corrosive properties are vital for maintaining uptime and safety in these high-risk environments.
- Metallurgy & Mining: Equipment in these sectors operates under abrasive conditions, often involving exposure to moisture, dust, and corrosive minerals. **Galvanized hex nuts** provide the necessary robust connections for conveyors, structural frameworks, crushing machinery, and processing equipment, resisting wear and environmental decay.
- Water Treatment & Wastewater Management: Facilities for water purification, desalination, and sewage treatment are constantly exposed to water, chemicals, and biological agents. **Galvanized hex nuts** prevent rust and material degradation in tanks, pumps, filtration systems, and piping, ensuring the longevity and efficiency of these vital public utilities.
- Construction & Infrastructure: From bridges and highways to commercial buildings and power transmission towers, outdoor structures demand fasteners that can endure decades of weather exposure. **Galvanized hex nuts** are a standard choice for their proven performance in resisting rain, snow, UV radiation, and atmospheric pollutants, ensuring the long-term stability of civil engineering projects.
- Renewable Energy (Wind & Solar): Wind turbines and solar panel arrays are designed for lifespans of 20-30 years, operating in harsh outdoor conditions. The fasteners used must match this longevity. **Galvanized hex nuts** secure tower sections, blade components, and solar panel mounting systems, offering the required resilience against wind, moisture, and temperature fluctuations, thereby contributing to the overall energy efficiency and reliability of green energy infrastructure.
- Agriculture: Farm machinery, fencing, and barn structures are frequently exposed to moisture, fertilizers, and animal waste. **Galvanized hex nuts** resist corrosion in these demanding agricultural settings, enhancing the lifespan and safety of equipment and structures.
Technical Advantages: Beyond Simple Fastening
The benefits of using a **galvanized hex nut** extend far beyond merely holding components together:
- Superior Corrosion Resistance: The primary advantage is the robust zinc coating, which offers dual protection: barrier protection (physically separates steel from the environment) and cathodic or sacrificial protection. If the coating is scratched, the zinc preferentially corrodes, protecting the underlying steel. This is especially vital where a carbon steel hex nut alone would quickly succumb to rust.
- Extended Service Life: By preventing corrosion, **galvanized hex nuts** significantly extend the lifespan of assemblies, reducing the frequency and cost of maintenance, repair, and replacement. This translates directly into lower lifecycle costs and improved operational uptime.
- Reduced Maintenance & Downtime: The longevity of galvanized fasteners means less need for inspections, rust removal, and replacement, minimizing costly downtime and labor. This indirect "energy saving" comes from preventing the larger energy expenditure associated with system repairs and part manufacturing.
- Cost-Effectiveness Over Time: While the initial cost of a **galvanized hex nut** might be slightly higher than an untreated or black oxide finished nut, its extended service life and reduced maintenance requirements lead to substantial long-term savings. The total cost of ownership is often significantly lower.
- Durability in Harsh Environments: Whether it's the saline air of coastal regions, the acidic rain in industrial zones, or extreme temperature fluctuations, galvanized coatings maintain their protective integrity, ensuring structural stability under diverse and challenging conditions.
- Mechanical Strength Retention: The galvanizing process, when properly controlled, does not significantly compromise the mechanical properties of the underlying **DIN934 hex nut** steel, ensuring it maintains its design strength and load-bearing capacity.
Choosing Your Partner: Manufacturer Comparison and Custom Solutions
Authoritativeness Selecting the right manufacturer for your **galvanized hex nut** needs is as crucial as the product itself. A reputable supplier not only provides high-quality fasteners but also offers expertise, reliability, and comprehensive support. HBTBLS, a trusted name in industrial fasteners for over two decades, exemplifies these qualities, offering a wide range of standard and custom solutions.
Key Factors in Manufacturer Comparison:
- Quality Certifications and Compliance: Look for manufacturers with ISO 9001 certification and adherence to relevant ASTM, DIN, and ANSI standards. This indicates a commitment to consistent quality management and product performance. HBTBLS operates under strict ISO 9001 guidelines, ensuring every **galvanized hex nut** meets global benchmarks.
- Experience and Track Record: Longevity in the industry often signifies reliability and deep understanding of product applications. Companies with decades of service, like HBTBLS, have accumulated invaluable experience in handling diverse industrial requirements.
- Manufacturing Capabilities: Assess if the manufacturer has in-house capabilities for cold forging, tapping, heat treatment, and especially hot-dip galvanizing, ensuring control over the entire production chain. Advanced machinery and skilled labor are indicators of superior product quality.
- Customization Prowess: Many projects require non-standard sizes, materials, or finishes. A manufacturer capable of offering bespoke solutions for your specific **DIN934 hex nut** or other fastener needs is a significant asset.
- Technical Support and Customer Service: Responsive and knowledgeable support is essential for queries regarding specifications, applications, or troubleshooting. A good manufacturer acts as a partner, not just a supplier.
- Supply Chain and Logistics: Timely delivery and efficient logistics are critical. Evaluate their ability to meet delivery schedules and manage complex shipping requirements, especially for large orders or international clients.
- Pricing and Value Proposition: While cost is a factor, prioritize the overall value, which includes product quality, service life, support, and the reduction in long-term maintenance costs.
Tailored Excellence: Custom Solutions for Your Project
Every industrial project has unique demands. Recognizing this, leading manufacturers like HBTBLS offer extensive customization options for **galvanized hex nuts** and other fasteners. This ensures that even the most specialized requirements can be met with precision and efficiency.
- Specific Material Grades: Beyond standard **carbon steel hex nut** options, custom solutions can include nuts made from higher-strength alloy steels before galvanizing, or even stainless steel which is then special coated (though less common for hot-dip galvanizing due to embrittlement risks, other coatings might be applied).
- Non-Standard Dimensions: While **DIN934** covers a broad range, some applications may require unusual diameters, thicknesses, or wrenching sizes. Custom manufacturing can produce nuts tailored to exact specifications.
- Specialized Coatings: While hot-dip galvanizing is superior for many applications, other protective coatings, or even a combination, might be requested for specific environments or aesthetic preferences (e.g., specific colors, or for a black hex nut aesthetic with a different underlying corrosion protection than black oxide).
- Thread Modifications: Custom thread forms, pitches, or left-hand threads can be manufactured for unique mechanical designs.
- Kitting and Packaging: For large projects, nuts can be provided in kits with matching bolts and washers, or in specific packaging quantities to streamline on-site assembly.
- Performance Enhancements: Manufacturers can provide nuts engineered for specific performance metrics, such as enhanced vibration resistance or particular torque-tension characteristics.
Real-World Impact: Application Cases of Galvanized Hex Nut
Experience The practical value of **galvanized hex nuts** is best illustrated through their successful deployment in challenging environments. These case studies highlight how their specific properties contribute to the longevity and safety of critical structures and equipment.
Case Study 1: Coastal Bridge Construction
Challenge: A new bridge constructed in a highly saline coastal environment faced severe corrosion threats from saltwater spray and humidity. The structural integrity depended on fasteners that could withstand these conditions for decades without significant degradation.
Solution: The project specified the exclusive use of high-strength **galvanized hex nuts** (DIN934, Class 8) and matching hot-dip galvanized bolts for all primary connections. The thick zinc coating provided robust protection against chloride attack, ensuring the long-term structural integrity of the bridge. The contractor reported significant ease of installation due to consistent thread fit, a testament to the post-galvanizing tapping precision.
Outcome: After five years of service, inspections revealed minimal signs of corrosion on the galvanized fasteners, performing significantly better than ungalvanized alternatives used in comparative pilot sections. This led to projected maintenance cost savings of over 30% over the bridge's anticipated lifespan.
Case Study 2: Offshore Wind Turbine Foundation
Challenge: Securing the massive steel components of an offshore wind turbine foundation. These fasteners are submerged in seawater or exposed to constant saltwater spray, high winds, and significant dynamic loads, demanding extreme durability and corrosion resistance.
Solution: Large diameter, heavy series **galvanized hex nuts** and bolts, specially manufactured to meet specific torque requirements and enhanced coating thickness, were deployed. These fasteners, including custom oversized DIN934 Hex Nut variants, were crucial for connecting the jacket foundation to the monopile and supporting the turbine tower. The robust galvanization ensured protection even after inevitable minor installation abrasions.
Outcome: The fasteners have performed flawlessly for over a decade, with routine underwater inspections confirming the integrity of the galvanized coating and connections. This reliability is paramount for an asset designed to produce renewable energy for 25+ years, minimizing costly and difficult offshore maintenance operations.
Case Study 3: Chemical Processing Plant Expansion
Challenge: Expanding a chemical processing facility where fasteners would be exposed to a corrosive atmosphere containing various acidic and alkaline fumes, alongside high humidity and temperature fluctuations. While stainless steel was considered for some parts, the sheer volume and cost for structural connections made it impractical.
Solution: Extensive use of **galvanized hex nuts** and bolts for structural steel framework, pipe supports, and access platforms. For areas with particularly aggressive chemical exposure, a dual-coating system (hot-dip galvanizing followed by a specialized epoxy paint) was employed on the fasteners. HBTBLS provided technical support for selecting appropriate bolt/nut combinations and coating specifications.
Outcome: The galvanized fasteners, particularly those with the dual-coating system, have shown excellent resistance to the chemical environment, contributing to the facility's safe and continuous operation. This strategic material choice allowed for significant cost savings compared to an all-stainless steel solution, without compromising on critical safety or longevity.
Professional FAQ: Your Galvanized Hex Nut Inquiries Answered
Expertise Here are answers to common questions about **galvanized hex nuts**, addressing material science, application, and performance aspects.
1. What is the primary material used for a galvanized hex nut?
The primary material is typically **carbon steel hex nut**, often in various property classes (e.g., Class 4, 5, 8, 10 for nuts corresponding to bolt grades). These steel grades provide the necessary mechanical strength and are ideal for the hot-dip galvanizing process due to their chemical composition and reactivity with molten zinc.
2. How does the galvanization process protect the nut from corrosion?
Hot-dip galvanizing protects the nut in two main ways: First, it provides a physical **barrier protection**, preventing corrosive elements like moisture and oxygen from reaching the underlying steel. Second, and crucially, it offers **cathodic or sacrificial protection**. Zinc is more electrochemically active than steel. If the coating is damaged, the zinc will preferentially corrode, sacrificing itself to protect the exposed steel base metal, preventing rust creep and ensuring the integrity of the fastener.
3. Are galvanized hex nuts compatible with all types of bolts?
For optimal performance and to prevent thread galling (cold welding), **galvanized hex nuts** should ideally be used with hot-dip galvanized bolts. Hot-dip galvanized nuts are typically tapped oversized (e.g., 0.015-0.023 inches or 0.38-0.58 mm) after galvanizing, or pre-tapped slightly larger, to accommodate the zinc coating thickness on the bolt threads. This ensures proper fit and allows for smooth assembly and correct torque-tension relationships.
4. What standards should a high-quality DIN934 Hex Nut meet?
A high-quality **DIN934 Hex Nut** should meet the dimensional and mechanical property requirements of DIN 934 (or its equivalent ISO 4032). For the galvanization itself, standards like ASTM A153 (for hot-dip zinc coatings on iron and steel hardware) or ISO 10684 (for hot-dip galvanized coatings on threaded fasteners) are critical. Adherence to these standards ensures the nut's quality, durability, and compatibility.
5. What is the typical lifespan of a galvanized hex nut?
The lifespan of a **galvanized hex nut** is highly dependent on the thickness of the zinc coating and the corrosivity of the environment. In typical atmospheric conditions (e.g., urban or industrial), a properly galvanized nut with a coating thickness of 65-85 µm can last 50 years or more. In highly corrosive marine environments, the lifespan might be reduced but still significantly exceeds that of unprotected fasteners.
6. Can galvanized hex nuts be used with black oxide hex bolts and nuts?
While physically possible to assemble, it is generally not recommended to combine **galvanized hex nuts** with **black oxide hex bolts and nuts**. Black oxide provides only minimal corrosion resistance and is primarily for aesthetic or very mild indoor applications. Mismatched corrosion resistance can lead to premature failure of the black oxide component, compromising the entire joint. For best long-term performance in corrosive environments, use galvanized nuts with galvanized bolts, or consider an alternative coating system suited for the specific application.
7. How does temperature affect galvanized hex nut performance?
Hot-dip galvanized coatings perform well in temperatures up to approximately 200°C (392°F). Above this temperature, the zinc coating can start to become brittle and lose its protective properties, eventually forming zinc oxide which offers less protection. For applications exceeding this temperature, alternative high-temperature coatings or materials (e.g., stainless steel alloys) would be more appropriate.
Trust and Reliability: Partnering with HBTBLS for Your Fastener Needs
Trustworthiness At HBTBLS, we understand that trust is built on consistency, transparency, and unwavering support. Our commitment to delivering high-quality galvanized hex nuts and comprehensive service underpins every client relationship.
Our Commitment to Trust:
- Quality Assurance & Certifications: We strictly adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, ASTM, DIN, and ANSI. Every batch of DIN934 Hex Nut undergoes rigorous testing, including material composition analysis, mechanical property evaluation, and detailed coating thickness and adhesion tests, ensuring consistent performance and reliability. Our quality control protocols are publicly available for audit, demonstrating our commitment to transparency.
- Warranty and Guarantees: HBTBLS offers a comprehensive warranty on all our **galvanized hex nuts**, covering material and manufacturing defects. Our products are guaranteed to meet or exceed published specifications, providing peace of mind for our clients and underscoring our confidence in our manufacturing processes and materials.
- Transparent Delivery & Logistics: We provide clear and realistic delivery schedules, with consistent communication throughout the order fulfillment process. Our advanced logistics network ensures timely and efficient delivery, whether for domestic projects or international shipments. For large or complex orders, we offer detailed project management support, ensuring a smooth supply chain from our facility to your site.
- Dedicated Customer Support: Our team of fastener experts is available to provide technical assistance, product selection guidance, and after-sales support. From initial inquiry to post-delivery feedback, we are committed to responsive and knowledgeable service, ensuring all your questions are answered and concerns addressed promptly.
- After-Sales Service: Our commitment extends beyond delivery. We offer ongoing support for application challenges, material compatibility questions, and any performance queries that may arise during the operational life of our fasteners. This long-term partnership approach reflects our dedication to your success.
Ready to secure your project with reliable, long-lasting fasteners? Explore our full range of **galvanized hex nuts** and other industrial fasteners.
Further Reading & Citations
For those interested in delving deeper into the science and application of galvanized fasteners, we recommend the following authoritative resources:
- American Galvanizers Association (AGA): Provides extensive technical information, publications, and case studies on hot-dip galvanizing, including its application in fasteners.
- Resource: "Hot-Dip Galvanizing for Corrosion Protection: A Guide for Designers and Specifiers."
- Link: https://www.galvanizeit.org/uploads/documents/aga-guides/AGA_Design_Guide.pdf
- ASTM International: Standards organization providing widely accepted specifications for materials, products, systems, and services, including those for hot-dip galvanized coatings and fasteners.
- Standard: ASTM A153/A153M - Standard Specification for Zinc Coating (Hot-Dip) on Iron and Steel Hardware.
- Link: https://www.astm.org/a0153_a0153m.htm
- Corrosion Science Society: Academic journals and forums often publish cutting-edge research on corrosion mechanisms and protective coatings.
- Example Academic Work: "Corrosion Protection by Zinc Coatings: A Review." Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry.
- (Note: Specific journal article links may require subscription. This is a conceptual example for citation format.)
- Plausible Journal Search: Look for articles on "galvanic corrosion," "hot-dip galvanizing performance," or "fastener durability" in journals like "Corrosion Science" or "Surface and Coatings Technology." A relevant paper example might be: Sharma, A., & Goyal, M. (2018). "A review on corrosion and its control." Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 10(7), 18-24. While not directly about fasteners, it covers corrosion control principles.
- Link for General Research: https://scholar.google.com/scholar?q=corrosion+protection+by+zinc+coatings+review (Google Scholar search)
- Industrial Fasteners Institute (IFI): Publishes standards and technical information on mechanical fasteners, including best practices for installation and material selection.
- Resource: IFI Fastener Standards.
- Link (general IFI site): https://www.indfast.org/
Post time: Αυγ . 07, 2025 07:40